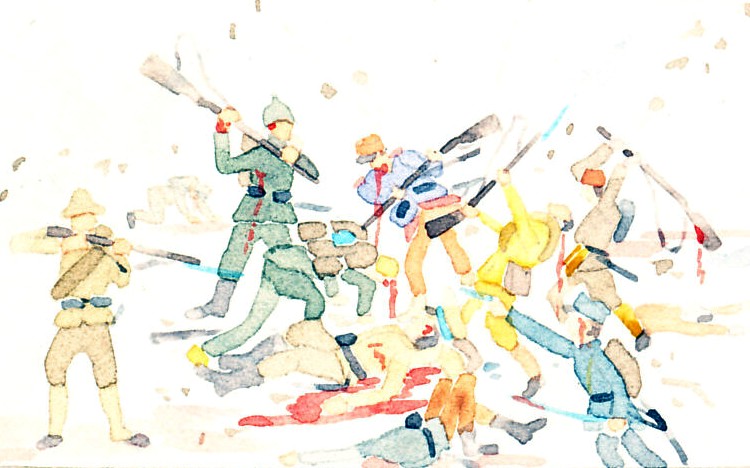
Battleships of the French War Navy in harbor including the Vergniaud, Edgard-Quinet, Mirabeau (in the distance), and Vérité.
Vergniaud and Mirabeau were 'semi-dreadnoughts' (Cuirassés d'Escadre) of the Danton class. Edgard-Quinet was a Croiseurs Cuirassés, an armoured cruiser. Vérité was a Cuirassé de deuxieme rang — a battleship of the second rank.
46 Marine de Guerre Française — Cuirassé sur rade
[Card] 46 French War Navy — Battleships in harbor
Vergniaud, Edgard-Quinet, Mirabeau, Vérité
Reverse:
Artaud et Nozais, Imp.-Édit., Nantes
Other views:
Larger
