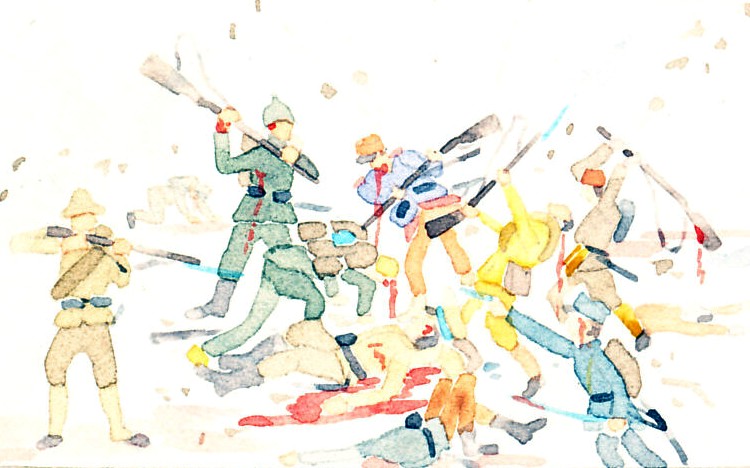
A Liebig bullion card from the series "Colonies of the European Powers" — The German colonies of Togo, Cameroon, and German East Africa, c1910.
Colonies des Puissances Européennes — Allemagne
Village au Cameroun.
Lomé (Togo).
Indegene du Cameroun.
Femme de l'Est Africain.
Véritable Extrait de Viande Liebig.
Voir L’Explication au verso.
Colonies of the European powers
Germany
Village in Cameroon.
Lome (Togo).
Indegene Cameroon.
Woman in East Africa.
Genuine Liebig Meat Extract.
See the explanation on the back.
Reverse:
Capital 27,000,000 Francs.
Établissements à Fray-Bentos (Uruguay) et Colon (Rép. Argentine).
Le véritable Extrait de viande Liebig transforme les sauces les plus fades, les rests de viande, en choses succulentes qui flattent délicieusement le palais.
Colonies des Puissances Européennes
Allemagne - Les premiers essais colonisateurs de l'Allemagne datent de l'époque du Grand Electeur. Ils furent infructeux. Ce n'est qu'en 1884 qu'elle entra dans la voie de ses devancières en fait de colonization. Angre Pequena, dans le Sud-ouest africain, fut sa première colonie; suiverent successivement le Togo, le Cameroun, la partie orientale de la Nouvelle-Guinée, l'archipel de Bismarck. En 1885, elle agrandit ses possessions africaines par l'adjonction de territoires dans l'Est du continent noir et annexa les Iles Marshall et Samoa, dans l'Océanie; elle prit à bail pour 99 ans la baie et la ville de Kiao-tchéou, en Chine. Les viguettes du recto de cette carte donnent des vues des principales possessions allemandes en Afrique. La population des colonies allemandes s'élève à plus de 12 millions, répartis sur une surface total de 2 millions et demi de kilomètres carrés.
Capital 27 million francs.
Institutions Fray Bentos (Uruguay) and Colon (Rep. Argentina).
The real meat extract Liebig transforms the most bland sauces, meat leftovers, into deliciously succulent things that flatter the palate.
Colonies of the European powers
Germany — The first German attempts at colonization date from the time of the Gre
Other views:
Larger, Back, LargerBack
